Gas chromatography is also used to monitor industrial processes automatically: gas streams are analyzed periodically and manual or automatic responses are made to counteract undesirable variations.
Many routine analyses are performed rapidly in environmental and other fields. For example, many countries have fixed moniotor points to continuously measure the emission levels of for instance nitrogen dioxides, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. Gas chromatography is also useful in the analysis of pharmaceutical products, alcohol in blood, essential oils and food products.
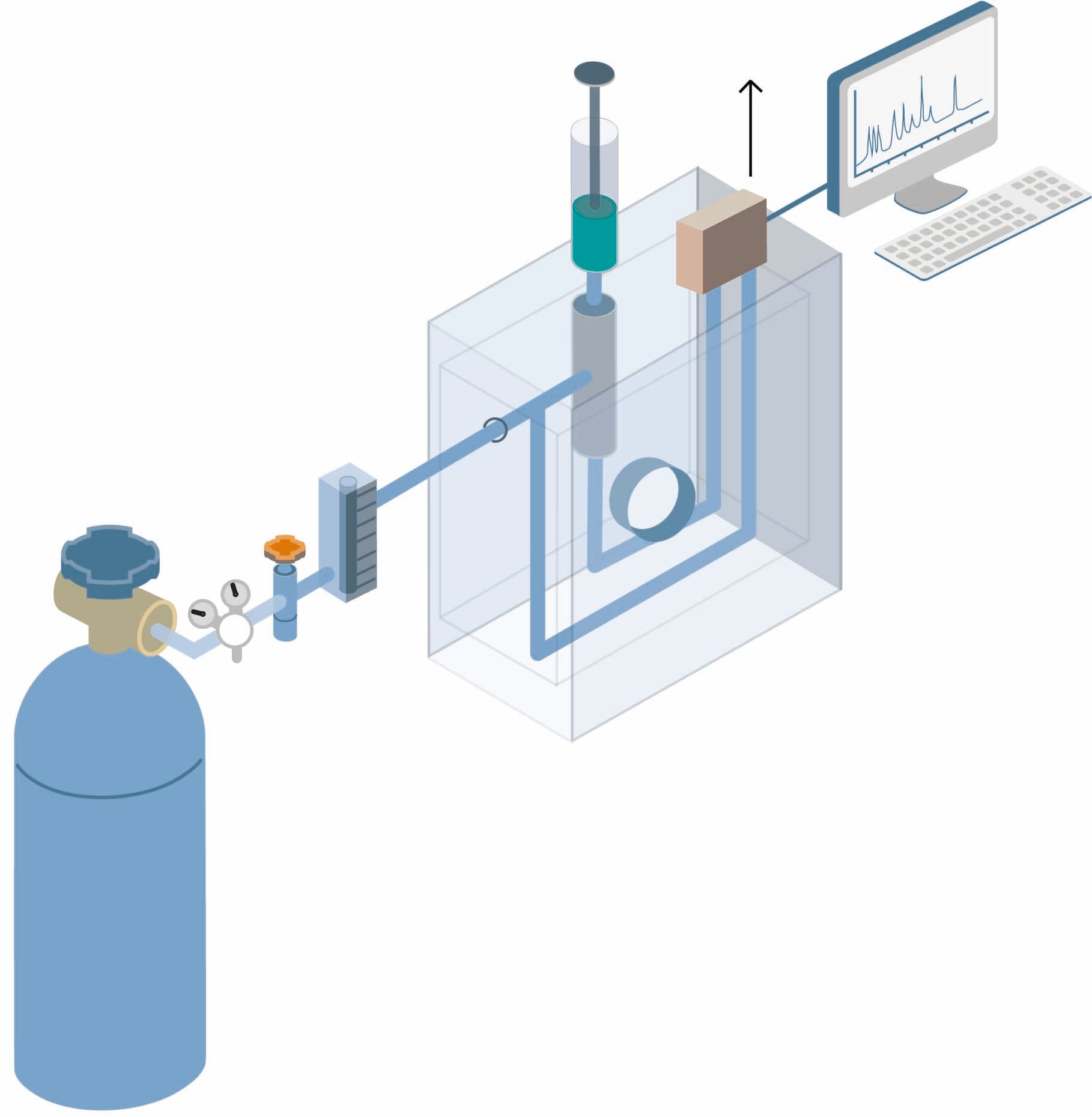
The method consists of, first, introducing the test mixture or sample into a stream of an inert gas, commonly helium or argon, that acts as carrier. Liquid samples are vaporized before injection into the carrier stream. The gas stream is passed through the packed column, through which the components of the sample move at velocities that are influenced by the degree of interaction of each constituent with the stationary nonvolatile phase. The substances having the greater interaction with the stationary phase are retarded to a greater extent and consequently separate from those with smaller interaction. As the components elute from the column they can be quantified by a detector and/or collected for further analysis.
Detector |
Hydrogen |
Helium |
Argon |
Nitrogen |
Methane / Argon Mixture |
Synthetic Air |
| FID | C/D | C/M | C/M | D | ||
| TCD | C/M | C/M | C | C/M | ||
| ECD | C | C | C/M | C/M | ||
| FPD | C/D | C | C | C/M | D | |
| NPD | D | C/M | C/M | D | ||
| PID | C/M | C/M | C/M |
* C: Carrier gas; D: Detector gas; M: Make up gas
Two types of gas chromatography are encountered: gas-solid chromatography (GSC) and gas-liquid chromatography (GLC). Gas-solid chromatography is based upon a solid stationary phase on which retention of analytes is the consequence of physical adsorption. Gas-liquid chromatography is useful for separating ions or molecules that are dissolved in a solvent. If the sample solution is in contact with a second solid or liquid phase, the different solutes will interact with the other phase to differing degrees due to differences in adsorption, ion-exchange, partitioning or size. These differences allow the mixture components to be separated from each other by using these differences to determine the transit time of the solutes through a column.
Gas Chromatography - Carrier gas
The choice of carrier gas depends on the type of detector that is used and the components that are to be determined. Carrier gases for chromatographs must be of high purity and chemically inert towards the sample e.g., helium (He), argon (Ar), nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen (H2). The carrier gas system can contain a molecular sieve to remove water or other impurities.
Sample injection system
The most common injection systems for introduction of gas samples are the gas sampling valve and injection with a syringe.
Direct injection with syringe
Both gaseous and liquid samples can be injected with a syringe. In the simplest form the sample is first injected into a heated chamber where it is vaporized before it is transferred to the column. When packed columns are used, the first part of the column often serves as injection chamber, separately heated to an appropriate temperature. For capillary columns a separate injection chamber is used from which only a small part of the vaporized/gaseous sample is transferred to the column, so called split-injection. This is necessary in order not to overload the column in regard to the sample volume.
When trace amounts can be found in the sample, so called on-column-injection can be used for capillary-GC. The liquid sample is injected directly into the column with a syringe. The solvent is thereafter allowed to evaporate and a concentration of the sample components takes place. If the sample is gaseous the concentration is achieved by so called cryo focusing. The sample components are concentrated and separated from the matrix by condensation in a cold-trap before the chromatographic separation.
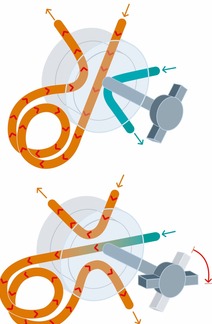
Injection with valve/sample loop. Loop-injection is often used in process control, where gaseous or liquid samples continuously flow through the sample loop. The sample loop is filled in off-line position with a syringe or an automatic pump. Thereafter the loop is connected in series with the column and the sample is transferred by the mobile phase. Sometimes a concentration step is necessary.